Terminal Tricks: Have Fun with the Linux Command Line
📅Hello, World! I put together this list of cool Linux terminal commands that can be yours today, for the low price of FREE!
Basic
Get the weather.
curl wttr.in
Copy a command output to the clipboard.
cat file.txt | xclip -sel clip
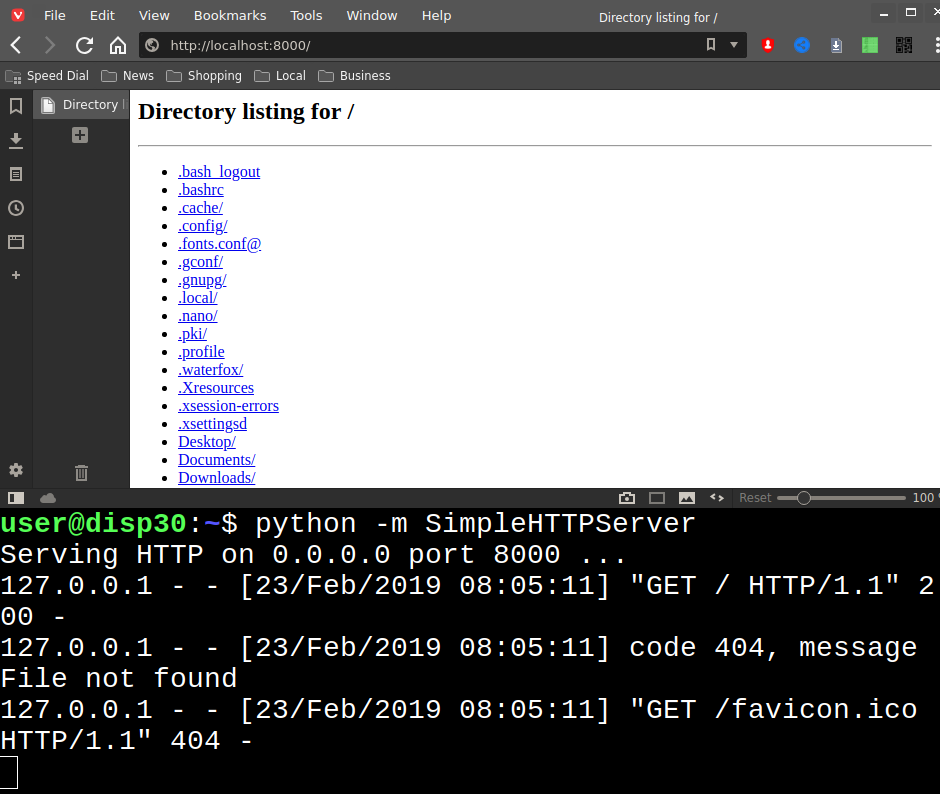
Serve the current directory on port 8000 as a web server.
python -m http.server
(The old way was python -m SimpleHTTPServer, which is how it is in the screenshot)
Visit the web server at http://localhost:8000/ in your browser. Press Ctrl-C in the terminal to stop the server.
python -m SimpleHTTPServer
A web server with one command! It can also be accessed by anyone on the same local network (house, school, library, etc.)
Measure the time it takes to run a command.
time find
Display a calendar.
cal
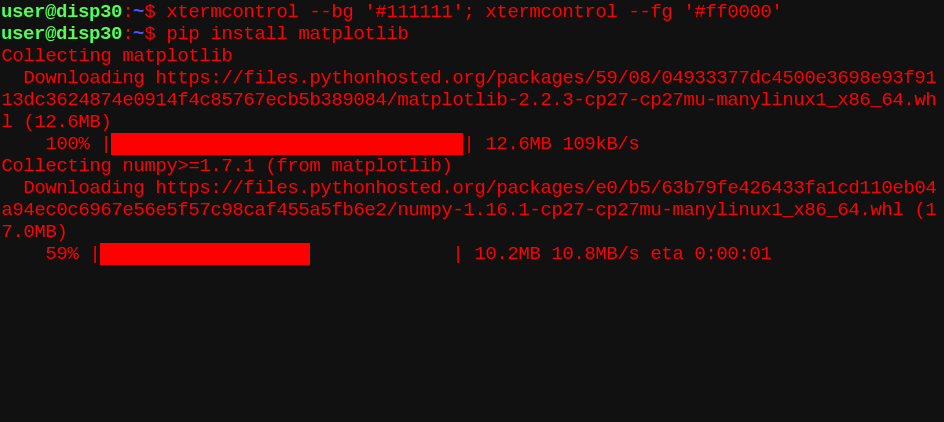
Change the terminal to attack mode!
xtermcontrol –bg ‘#111111’; xtermcontrol –fg ‘#ff0000’
Terminal with Red Text
Installing a python package in attack mode!
Re-run the last command as root.
sudo !!
Exit the terminal but leave all processes running.
disown -a && exit
Open a webpage in a text-based browser. Use the arrow keys to navigate, ENTER to click on links, and Shift+B to go back.
w3m duckduckgo.com?q=Terminal+Tricks
Advanced
Set up a Virtual Private Network (VPN) on a remote server such as a DigitalOcean droplet. This will create a file /root/client.ovpn which tells other computers how to connect to the remote server.
user@local:~$ ssh root@remote
root@remote:~$ wget https://git.io/vpn -O openvpn.sh && sudo bash openvpn.sh
Copy the client.ovpn file to the local machine.
user@local:~$ scp root@remote:/root/client.ovpn .
Import the remote openvpn server config into NetworkManager on Linux.
user@local:~$ nmcli connection import type openvpn file client.ovpn
Then use the network system tray icon to connect to the server.
Scan the local network an get a list of the devices, their IP addresses, and mac addresses. Replace “wlan0” with your network device, which you can find with “ip a”. The “tee” command saves the output to a file, while also displaying it to the terminal.
sudo arp-scan –localnet –interface=wlan0 | tee arp-scan.txt
Log in to a Raspberry Pi whose default password has not been changed. Replace the IP address with the actual IP address of the Pi. Let this serve as a warning: Be sure to change your Pi passwords so random folks don’t log in!
ssh pi@192.168.1.99
Password: raspberry
Scan a computer on the network for open ports and other info.
sudo nmap -v 192.168.1.99
Forward local port 3337 to a remote server’s port 6379.
ssh -L 3337:localhost:6379 username@hostname
Set up a proxy on the local port 8000 through a remote server.
ssh -CND 8000 username@hostname
Set your web browser’s proxy settings to “localhost” and “8000” to act as if it was in the same local network as the server.
Surprises…
curl -s http://artscene.textfiles\.com/vt100/globe.vt | pv -L9600 -q
telnet towel.blinkenlights.nl
sl
Big thanks to the internet, including but not limited to climagic and this youtube video.